Parameter Definition |
Example |
Wavelength Range (nm) is the spectral range over which the optical interleaver's optical performance can be met. |
1530.33 - 1563.05 nm |
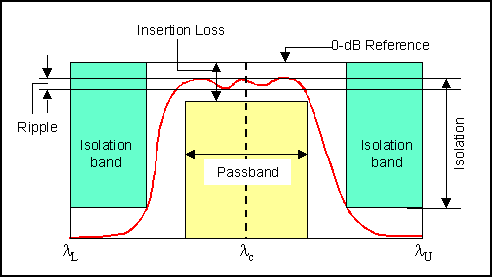
Insertion Loss (dB) is the relative
power level transmitted to the output ports referenced to the 0-dB level when
the optical interleaver is inserted. It is the
power difference between the 0-dB level and the minimum power level measured
within a given passband window. See figure below. |
1.5 dB |
Ripple (dB) is defined as the power difference
between the minimum loss and the maximum loss within a given passband. |
0.3 dB |
Passband Bandwidth (GHz) is defined as the spectral width centered at ITU grid at a given
power level, typically at 0.5 dB below the minimum insertion loss point. |
ITU ± 30 GHz |
Isolation (dB) is defined as the power difference
between maximum insertion loss measured within a given passband window and the minimum insertion loss measured within the adjacent stopband window |
24 dB |
|
|
Insertion Loss Uniformity (dB) is the
difference between the maximum insertion loss and minimum insertion loss over
all channels, either within one output port or both ports. |
0.3 dB |
Polarization
Dependent Loss (PDL) (dB) is the difference
between the maximum and minimum insertion loss over all polarization states
within a given passband window. |
0.3 dB |
Chromatic
Dispersion (CD) (ps/nm)
is the derivative of the Group Delay versus wavelength within a given passband width. |
24 ps/nm within ITU±20%FSR |
Polarization
Mode Dispersion (PMD) (ps)
is the maximum Differential Group Delay within a given passband width. |
0.2 ps within ITU±30%FSR |
Optical
Return Loss (dB) is the ratio between the input
power and the reflected power over all polarization states at each port , RL = -10×log10(Pr/Pin). |
40 dB |
Operating
Temperature (°C) is the ambient temperature
range over which the device's performance spec can be met. |
-5 to 65 °C |
Storage
Temperature (°C) is the ambient temperature
range over which the device can be stored without affecting its intended
application afterwards. |
-40 to 85 °C |